This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| East Franconian | |
|---|---|
| Fränggisch[1] Standard High German: Ostfränkisch, Fränkisch | |
| Native to | Germany (Bavaria, Thuringia, Saxony, Baden-Württemberg, Hesse) |
Native speakers | 4,900,000 (2006)[2] |
Early forms | Proto-Indo-European
|
| Latin (German alphabet) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | vmf |
| Glottolog | main1267 |
| Linguasphere | 52-ACB-dj |
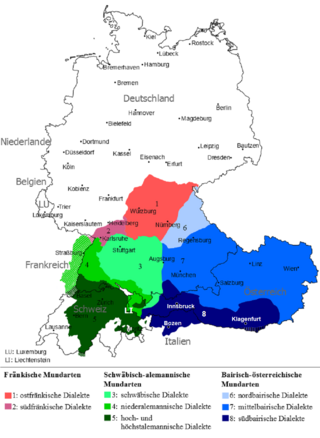 1: East Franconian | |
 East Franconian is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
East Franconian (German: Ostfränkisch [ˈɔstfʁɛŋkɪʃ] ), usually referred to as Franconian (Fränkisch [ˈfʁɛŋkɪʃ] ) in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are Unterostfränkisch (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), Oberostfränkisch (spoken in Upper and Middle Franconia) and Südostfränkisch (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe).

In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg. East Franconian is one of the German dialects with the highest number of speakers.
The scope of East Franconian is disputed, because it overlaps with neighbouring dialects like Bavarian and Swabian in the south, Rhine Franconian in the west and Upper Saxon in the north.
East Franconian is researched by the "Fränkisches Wörterbuch" project in Fürth, which is run by Bayerische Akademie der Wissenschaften and Erlangen-Nuremberg University.
- ^ Gerhard Fink and Langenscheidt-Redaktion (ed.), Langenscheidt Lilliput Fränkisch, Langenscheidt: München, 2018, p. 339: "Fränkisch is Fränggisch"
- ^ East Franconian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)