| Egg cell | |
|---|---|
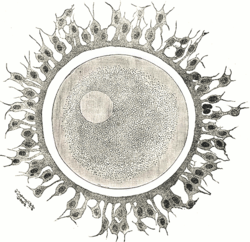 A human egg cell with surrounding corona radiata | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ovum |
| Greek | ωάριο (oário) |
| MeSH | D010063 |
| FMA | 67343 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy | |

The egg cell or ovum (pl.: ova) is the female reproductive cell, or gamete,[1] in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is not capable of movement (non-motile). If the male gamete (sperm) is capable of movement, the type of sexual reproduction is also classified as oogamous. A nonmotile female gamete formed in the oogonium of some algae, fungi, oomycetes, or bryophytes is an oosphere.[2] When fertilized, the oosphere becomes the oospore.[clarification needed]
When egg and sperm fuse during fertilisation, a diploid cell (the zygote) is formed, which rapidly grows into a new organism.
- ^ "Ovum". Biology Dictionary. BiologyOnline. 7 October 2019. Retrieved 21 January 2023.
- ^ "Oosphere Meaning". YourDictionary. Retrieved 12 April 2021.