 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Perlutal, Topasel, Unalmes, Yectames, others |
| Other names | EEn; E2-EN; EE; E2E; Estradiol enanthate; Estradiol heptanoate; SQ-16150 |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection[1][2] |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | IM: High |
| Protein binding | Estradiol: ~98% (to albumin and SHBG)[3][4] |
| Metabolism | Cleavage via esterases in the liver, blood, and tissues[5][6] |
| Metabolites | Estradiol, heptanoic acid, and metabolites of estradiol[5][6] |
| Elimination half-life | IM: 5.6–7.5 days[7][1][8][9] |
| Duration of action | IM (10 mg): ~20–30 days[10][5] |
| Excretion | Urine[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.272 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
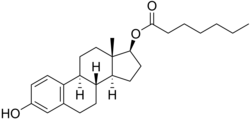
| Formula | C25H36O3 |
| Molar mass | 384.560 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Estradiol enantate (EEn or E2-EN), also spelled estradiol enanthate and sold under the brand names Perlutal and Topasel among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormonal birth control for women.[1][2][11] It is formulated in combination with dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide (DHPA; algestone acetophenide), a progestin, and is used specifically as a combined injectable contraceptive.[1][2] Estradiol enantate is not available for medical use alone.[12][13][14][15] The medication, in combination with DHPA, is given by injection into muscle once a month.[1][2]
Side effects of estradiol enantate include breast tenderness, breast enlargement, nausea, headache, and fluid retention.[16] Estradiol enantate is an estrogen and hence is an agonist of the estrogen receptor, the biological target of estrogens like estradiol.[6][5] It is an estrogen ester and a long-lasting prodrug of estradiol in the body.[5][6] Because of this, it is considered to be a natural and bioidentical form of estrogen.[5][17]
Estradiol enantate was first described by 1954,[18] and was first studied in combination with DHPA as a combined injectable contraceptive in 1964.[19][20] The combination was introduced for clinical use by the mid-1970s.[21][22][23] Estradiol enantate is not available as a standalone medication (i.e., by itself without DHPA).[15] The combination is available in Latin America and Hong Kong, and was also previously marketed in Spain and Portugal.[15][2][13]
- ^ a b c d e f Jarquín González JD, Elda de Aguirre L, Rodríguez C, Abrego de Aguilar M, Carrillo F, León DA, et al. (September 1996). "Dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide 150 mg + estradiol enantate 10 mg as monthly injectable contraceptives". Advances in Contraception. 12 (3): 213–225. doi:10.1007/BF01849664. PMID 8910663. S2CID 2522426.
- ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
pmid12290848was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Stanczyk FZ, Archer DF, Bhavnani BR (June 2013). "Ethinyl estradiol and 17β-estradiol in combined oral contraceptives: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and risk assessment". Contraception. 87 (6): 706–727. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2012.12.011. PMID 23375353.
- ^ Falcone T, Hurd WW (2007). Clinical Reproductive Medicine and Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 22, 362, 388. ISBN 978-0-323-03309-1.
- ^ a b c d e f Oettel M, Schillinger E (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens II: Pharmacology and Clinical Application of Estrogens and Antiestrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 261, 271. ISBN 978-3-642-60107-1.
Natural estrogens considered here include: [...] Esters of 17β-estradiol, such as estradiol valerate, estradiol benzoate and estradiol cypionate. Esterification aims at either better absorption after oral administration or a sustained release from the depot after intramuscular administration. During absorption, the esters are cleaved by endogenous esterases and the pharmacologically active 17β-estradiol is released; therefore, the esters are considered as natural estrogens. [...] Wiemeyer et al. (1986) measured elevated estradiol levels up to 31 days after an intramuscular dose of 10mg estradiol enanthate.
- ^ a b c d Kuhl H (August 2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration". Climacteric. 8 (Suppl 1): 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947. S2CID 24616324.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid3814225was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid8013220was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Bula do Algestona Acetofenida + Enantato de Estradiol". Consulta Remédios. Archived from the original on 18 September 2018. Retrieved 18 September 2018.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid8013219was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Bagade O, Pawar V, Patel R, Patel B, Awasarkar V, Diwate S (2014). "Increasing use of long-acting reversible contraception: safe, reliable, and cost-effective birth control" (PDF). World J Pharm Pharm Sci. 3 (10): 364–392. ISSN 2278-4357.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Martindalewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Micromedexwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Drugs.comwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
IndexNominum2000was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ghosh2010was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Arun N, Narendra M, Shikha S (15 December 2012). Progress in Obstetrics and Gynecology--3. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Pvt. Ltd. pp. 419–. ISBN 978-93-5090-575-3.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Symposium1954was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid14236841was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid14236842was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
BringerHedon1995was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid865726was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid8013216was invoked but never defined (see the help page).