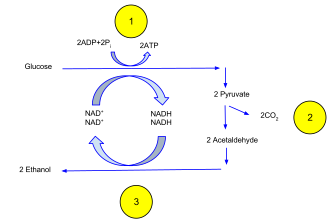
Ethanol fermentation, also called alcoholic fermentation, is a biological process which converts sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose into cellular energy, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide as by-products. Because yeasts perform this conversion in the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation is considered an anaerobic process. It also takes place in some species of fish (including goldfish and carp) where (along with lactic acid fermentation) it provides energy when oxygen is scarce.[1]
Ethanol fermentation is the basis for alcoholic beverages, ethanol fuel and bread dough rising.
- ^ Aren van Waarde; G. Van den Thillart; Maria Verhagen (1993). "Ethanol Formation and pH-Regulation in Fish". Surviving Hypoxia. pp. 157−70. hdl:11370/3196a88e-a978-4293-8f6f-cd6876d8c428. ISBN 978-0849342264.