 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌɛθklɔːrˈvaɪnɒl/ ETH-klor-VY-nol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 35–50% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.239.078 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
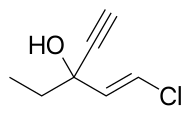
| Formula | C7H9ClO |
| Molar mass | 144.60 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Ethchlorvynol is a GABA-ergic sedative and hypnotic/soporific medication first developed by Pfizer in the 1950s.[4] In the United States it was sold by Abbott Laboratories under the trade name Placidyl.[2] Placidyl was available in 200 mg, 500 mg, and 750 mg strength gel filled capsules. While the 500 mg and 750 mg strength capsules were for use in reducing sleep latency, the 200 mg strength capsules were intended to be used to re-induce sleep in case of early awakening. Abbott discontinued production in 1999, due to it being replaced by the benzodiazepine family and its widespread abuse,[2] after which Placidyl was available for about a year in the United States. Although, theoretically, ethchlorvynol could be manufactured for sale in the United States by another pharmaceutical company (subject to FDA approval of such manufacture), no pharmaceutical company has chosen to do so. Individuals with a valid prescription for the substance may legally transport a reasonable amount of ethclorvynol with them into the United States.
- ^ Anvisa (31 March 2023). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 4 April 2023). Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ a b c "Erowid Ethchlorvynol Vault". Erowid. 12 January 2007. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ "Annual Statistical Report on Substances Listed in the Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 Form P" (PDF). International Narcotics Control Board (INCB). January 2014. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 September 2015. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ US 2746900, Bavley A, McLamore WM, "Hypnotic Agent and Method of Making the Same", issued 1956