| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
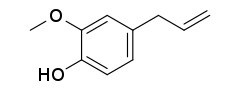
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methoxy-4-(prop-2-en-1-yl)phenol | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1366759 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.355 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 164.204 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.06 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −7.5 °C (18.5 °F; 265.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 254 °C (489 °F; 527 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.19 at 25 °C |
| −1.021×10−4 cm3/mol | |
| Viscosity |
|
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 104 °C (219 °F; 377 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
2-Phenethyl propionate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Eugenol /ˈjuːdʒɪnɒl/ is an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol, a member of the allylbenzene class of chemical compounds.[2] It is a colorless to pale yellow, aromatic oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove, nutmeg, cinnamon, basil and bay leaf.[3][4][5][6] It is present in concentrations of 80–90% in clove bud oil and at 82–88% in clove leaf oil.[7] Eugenol has a pleasant, spicy, clove-like scent.[8] The name is derived from Eugenia caryophyllata, the former Linnean nomenclature term for cloves. The currently accepted name is Syzygium aromaticum.[9]
- ^ Bingham EC, Spooner LW (1932). "The Fluidity Method for the Determination of Association. I". Journal of Rheology. 3 (2): 221–244. Bibcode:1932JRheo...3..221B. doi:10.1122/1.2116455. ISSN 0097-0360.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pubchemwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Constituents of the essential oil from leaves and buds of clove (Syzigium caryophyllatum L.) Alston" (PDF). Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research BCSIR Laboratories. 4: 451–454.
- ^ Mallavarapu GR, Ramesh S, Chandrasekhara RS, Rajeswara Rao BR, Kaul PN, Bhattacharya AK (1995). "Investigation of the essential oil of cinnamon leaf grown at Bangalore and Hyderabad". Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 10 (4): 239–242. doi:10.1002/ffj.2730100403.
- ^ Yield and Oil Composition of 38 Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Accessions Grown in Mississippi Archived 15 October 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Typical G.C. for bay leaf oil". Thegoodscentscompany.com. Archived from the original on 17 March 2014. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- ^ Barnes J, Anderson LA, Phillipson JS (2007) [1996]. Herbal Medicines (PDF) (3rd ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0-85369-623-0. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 July 2018. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ Wishart, David S.; Guo, An Chi; Oler, Eponine; et al. "Showing metabocard for Eugenol (HMDB0005809)". Human Metabolome Database, HMDB. 5.0.
- ^ Cortés Rojas DF, de Souza CR, Oliveira WP (February 2014). "Clove (Syzygium aromaticum): a precious spice". Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine. 4 (2): 90–6. doi:10.1016/S2221-1691(14)60215-X. PMC 3819475. PMID 25182278.
