| European pied flycatcher | |
|---|---|

| |
| Adult male in Scotland | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Muscicapidae |
| Genus: | Ficedula |
| Species: | F. hypoleuca
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ficedula hypoleuca (Pallas, 1764)
| |
| |
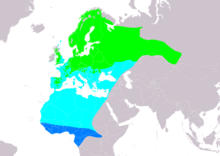
| Range of F. hypoleuca Breeding Passage Non-breeding
| |
| Synonyms | |
The European pied flycatcher (Ficedula hypoleuca) is a small passerine bird in the Old World flycatcher family. One of the four species of Western Palearctic black-and-white flycatchers, it hybridizes to a limited extent with the collared flycatcher.[3] It breeds in most of Europe and across the Western Palearctic. It is migratory, wintering mainly in tropical Africa.[1][4] It usually builds its nests in holes on oak trees.[5] This species practices polygyny, usually bigamy, with the male travelling large distances to acquire a second mate. The male will mate with the secondary female and then return to the primary female in order to help with aspects of child rearing, such as feeding.[3][6]
The European pied flycatcher is mainly insectivorous, although its diet also includes other arthropods. This species commonly feeds on spiders, ants, bees and similar prey.[7]
The European pied flycatcher has a very large range and population size and so it is of least concern according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).[1]
- ^ a b c BirdLife International. (2018). "Ficedula hypoleuca". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22709308A131952521. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22709308A131952521.en. Retrieved 24 June 2024.
- ^ Gould, John (1837). The Birds of Europe. Vol. 2. (Plate 63 and following text)
- ^ a b Silverin, Bengt (1980). "Effects of long-acting testosterone treatment on freeliving pied flycatchers, Ficedula hypoleuca, during the breeding period". Animal Behaviour. 28 (3): 906–912. doi:10.1016/s0003-3472(80)80152-7. ISSN 0003-3472. S2CID 53177170.
- ^ Robinson, R.A. (2005). "Pied Flycatcher Ficedula hypoleuca". BTO BirdFacts. British Trust for Ornithology. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- ^ "RSPB Pied Flycatcher Information Page". RSPB. Retrieved 24 September 2013.
- ^ von Haartman, Lars (1951). "Successive Polygamy". Behaviour. 3 (4): 256–274. doi:10.1163/156853951x00296.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Silverinawas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
