| Extraocular muscles | |
|---|---|
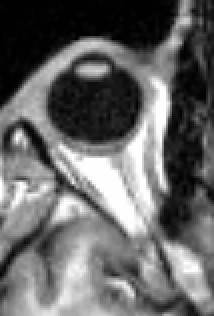 | |
| Details | |
| System | Visual system |
| Origin | Common tendinous ring, maxillary and sphenoid bone |
| Insertion | Tarsal plate of upper eyelid, eye |
| Artery | Ophthalmic artery, lacrimal artery, infraorbital artery, anterior ciliary arteries, superior and inferior orbital veins |
| Nerve | Oculomotor, trochlear and abducens nerve |
| Actions | See table |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculi externi bulbi oculi |
| MeSH | D009801 |
| TA98 | A04.1.01.001 |
| TA2 | 2041 |
| FMA | 49033 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in humans and other animals.[1] Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye. The other muscle, the levator palpebrae superioris, controls eyelid elevation. The actions of the six muscles responsible for eye movement depend on the position of the eye at the time of muscle contraction.[2]
The ciliary muscle, pupillary sphincter muscle and pupillary dilator muscle sometimes are called intrinsic ocular muscles[3] or intraocular muscles.[4]
- ^ Shumway, Caleb L.; Motlagh, Mahsaw; Wade, Matthew (2022). "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Eye Extraocular Muscles". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30137849. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ "Extrinsic eye muscle definition and meaning | Collins English Dictionary". www.collinsdictionary.com. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ Kels, Barry D.; Grzybowski, Andrzej; Grant-Kels, Jane M. (March 2015). "Human ocular anatomy". Clinics in Dermatology. 33 (2): 140–146. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2014.10.006. PMID 25704934.
- ^ Ludwig, Parker E.; Aslam, Sanah; Czyz, Craig N. (2024). "Anatomy, Head and Neck: Eye Muscles". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29262013.