| Fetal circulation | |
|---|---|
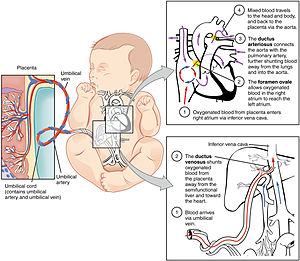 The fetal circulatory system includes three shunts to divert blood from undeveloped and partially functioning organs, as well as blood supply to and from the placenta. | |
| Details | |
| Gives rise to | Circulatory system |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In humans, the circulatory system is different before and after birth. The fetal circulation is composed of the placenta, umbilical blood vessels encapsulated by the umbilical cord, heart and systemic blood vessels. A major difference between the fetal circulation and postnatal circulation is that the lungs are not used during the fetal stage resulting in the presence of shunts to move oxygenated blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetal tissue. At birth, the start of breathing and the severance of the umbilical cord prompt various changes that quickly transform fetal circulation into postnatal circulation.[1][2]
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Development of organ systems |
|---|
- ^ "Comprehensive Perinatal & Pediatric Respiratory Care | R2 Digital Library". www.r2library.com. Retrieved 2022-09-12.
- ^ Marty, Makenna; Kerndt, Connor C.; Lui, Forshing (2022), "Embryology, Fetal Circulation", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30725834, retrieved 2022-09-12