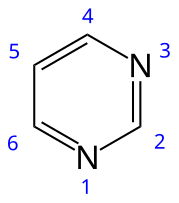
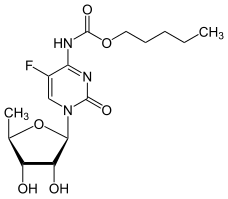
Left: The structure of pyrimidine with the locants for ring atoms marked. Right: 5-Fluorouracil, a fluoropyrimidine formally named as 5-fluoro-1H,3H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione
Fluoropyrimidines are a general class organic compounds in which the substituent(s) around a pyrimidine ring include at least one fluorine atom. The term "fluoropyrimidines" is often used more specifically to refer to the subset of this class that are antimetabolites and are used as anticancer medications, which include:
- Capecitabine
- Carmofur (HCFU)
- Doxifluridine
- Fluorouracil (5-FU)
- Tegafur
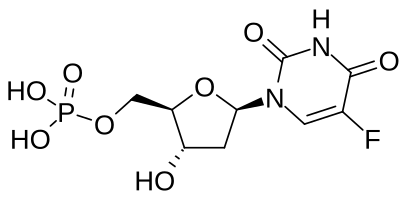
Some metabolites of these drugs, such as 5-fluorodeoxyuridylate monophosphate, also have fluoropyrimidine structures in the general sense of the term, but the more specific meaning is typically reserved for substances used as pharmaceuticals.
Left: The structure of capecitabine, a fluoropyrimidine drug with four substituents around its core pyrimidine ring. Right: 5-Fluorodeoxyuridylate monophosphate, a metabolite formed from 5-fluorouracil and 5-fluorodeoxyuridine, which includes a fluoropyrimidine moiety.