 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Dalmane, Dalmadorm, Fluzepam |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682051 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Addiction liability | Moderate |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Benzodiazepine |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 83% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Metabolites | N-desalkylflurazepam (active metabolite) |
| Elimination half-life | 2.3 hours N-desalkylflurazepam: 47–100 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.795 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
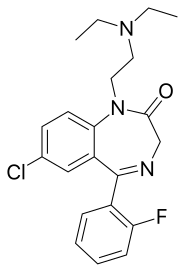
| Formula | C21H23ClFN3O |
| Molar mass | 387.88 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 79.5 °C (175.1 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Flurazepam[2] (marketed under the brand names Dalmane and Dalmadorm) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It produces a metabolite with a long half-life, which may stay in the bloodstream for days.[3] Flurazepam was patented in 1968 and came into medical use the same year.[4] Flurazepam, developed by Roche Pharmaceuticals, was one of the first benzodiazepine hypnotic medications to be marketed.[5]
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ BE 629005
- ^ "FLURAZEPAM HCl CAPSULES, USP". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 538. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ Shorter E (2005). "B". A Historical Dictionary of Psychiatry. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-029201-0.