Great Shu / Han 大蜀 / 漢 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 907–925 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Capital | Chengdu | ||||||||
| Common languages | Ba–Shu Chinese | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||
• 907–918 | Wang Jian | ||||||||
• 918–925 | Wang Zongyan | ||||||||
| Historical era | Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period | ||||||||
• Foundation of the State of Shu under Tang rule | 903 | ||||||||
• Fall of the Tang dynasty | June 1, 907 907 | ||||||||
• Ended by the Later Tang | 925 925 | ||||||||
| Currency | Chinese coin, Chinese cash | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | China | ||||||||
Shu had changed its country name from "Shu" to "Han" in 917–918. | |||||||||

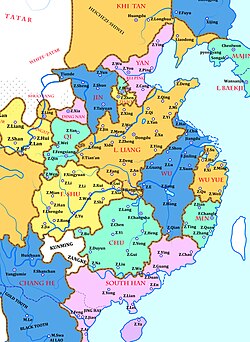
Great Shu (Chinese: 大蜀; pinyin: Dàshǔ), known in historiography as the Former Shu (Chinese: 前蜀; pinyin: Qiánshǔ) or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It existed from 907 to 925 CE.
The country's name changed from "Shu" to "Han" (Chinese: 漢; pinyin: Hàn) in 917–918, which is not to be confused with another contemporaneous kingdom during the same Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, the Southern Han (traditional Chinese: 南漢; simplified Chinese: 南汉; pinyin: Nán Hàn), 917–971 CE.