 | |
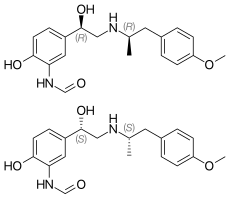
 Formoterol (top), (R,R)-(−)-formoterol (center) and (S,S)-(+)-formoterol (bottom) | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Oxeze, Foradil, Symbicort, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation (capsules for oral inhalation, DPI, MDI) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 61% to 64% |
| Metabolism | Liver demethylation and glucuronidation (CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and CYP2A6 involved) |
| Elimination half-life | 10 h |
| Excretion | Kidney and fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.131.654 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H24N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 344.411 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Formoterol, also known as eformoterol, is a long-acting β2 agonist (LABA) used as a bronchodilator in the management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Formoterol has an extended duration of action (up to 12 h) compared to short-acting β2 agonists such as salbutamol (albuterol), which are effective for 4 h to 6 h. Formoterol has a relatively rapid onset of action compared to other LABAs, and is effective within 2-3 minutes.[2] The 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma report [3] recommends a combination formoterol/inhaled corticosteroid inhaler as both a preventer and reliever treatment for asthma in adults. In children, a short-acting β2 adrenergic agonist (e.g., salbutamol) is still recommended.
It was patented in 1972 and came into medical use in 1998.[4] It is available as a generic medication.[5] It is also marketed in the combination formulations budesonide/formoterol and mometasone/formoterol.
- ^ "List of nationally authorised medicinal products" (PDF). ema.europa.eu. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- ^ Anderson GP (1993). "Formoterol: pharmacology, molecular basis of agonism, and mechanism of long duration of a highly potent and selective beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist bronchodilator". Life Sci. 52 (26): 2145–60. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(93)90729-m. PMID 8099696.
- ^ Global Initiative for Asthma (2022). Global Strategy for Asthma Prevention and Management (Updated 2022) (PDF) (Report).
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 543. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "Competitive Generic Therapy Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 29 June 2023. Archived from the original on 29 June 2023. Retrieved 29 June 2023.