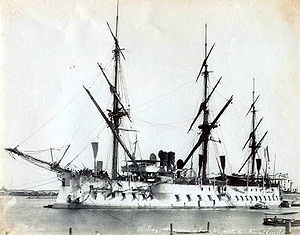
 Bayard crossing the Suez Canal at Port Said while bringing the remains of Admiral Amédée Courbet back to France. Her spars are set diagonally, one mast perpendicular to another, as a sign of mourning.
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Bayard |
| Namesake | Pierre Terrail, seigneur de Bayard |
| Builder | Brest |
| Laid down | 19 September 1876 |
| Launched | 27 March 1880 |
| Commissioned | November 1882 in Brest |
| In service | May 1883 |
| Stricken | 26 April 1899 |
| Fate | Broken up in 1910 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Bayard-class ironclad |
| Displacement | 6,363 t (6,263 long tons; 7,014 short tons) |
| Length | 81.22 m (266 ft 6 in) lwl |
| Beam | 17.45 m (57 ft) |
| Draft | 7.49 m (24 ft 7 in) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | |
| Sail plan | Full-ship rig |
| Speed | 14 knots (26 km/h; 16 mph) |
| Crew |
|
| Armament |
|
| Armor | |
Bayard was the lead ship of the Bayard class of ironclad barbette ships built for the French Navy in the late 1870s and 1880s. Intended for service in the French colonial empire, she was designed as a "station ironclad", smaller versions of the first-rate vessels built for the main fleet. The Vauban class was a scaled down variant of Amiral Duperré. They carried their main battery of four 240 mm (9.4 in) guns in open barbettes, two forward side-by-side and the other two aft on the centerline. Bayard was laid down in 1876 and was commissioned in 1882.