| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
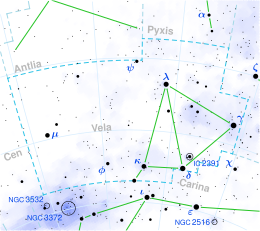
| Constellation | Vela |
| Right ascension | 08h 09m 31.95013s[1] |
| Declination | –47° 20′ 11.7108″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 1.83[2] (1.81–1.87[3]) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | WC8 + O7.5III[4] |
| U−B color index | −0.94[2] |
| B−V color index | −0.25[2] |
| Variable type | Wolf–Rayet[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +12 ± 1[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: –6.07[1] mas/yr Dec.: +10.43[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.92 ± 0.30 mas[1] |
| Distance | 1096+26 −23 ly (336+8 −7 [6] pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −4.6 + −6.0 [6] |
| Orbit[7] | |
| Primary | O |
| Companion | WR |
| Period (P) | 78.53 ± 0.01 days |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 1.2[8] AU |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.326 ± 0.01 |
| Inclination (i) | 65 ± 8° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,450,120.5 ± 2 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 248 ± 4° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 38.4 ± 2 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 122 ± 2 km/s |
| Details | |
| WR | |
| Mass | 9.0 ± 0.6 [8] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.9[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 204,000[6] L☉ |
| Luminosity (visual, LV) | 5,900[6] L☉ |
| Temperature | 90,000[6] K |
| Age | 5[6] Myr |
| O | |
| Mass | 28.5 ± 1.1[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 16.2[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 363,000[6] L☉ |
| Luminosity (visual, LV) | 21,500[6] L☉ |
| Temperature | 35,100[6] K |
| Age | 5[6] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Vela |
| Right ascension | 08h 09m 29.3260s[9] |
| Declination | –47° 20′ 43.027″[9] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.27[10] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B2III[11] |
| U−B color index | −0.92[10] |
| B−V color index | −0.22[10] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +9.7 ± 1[10] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: –0.6[12] mas/yr Dec.: +9.7[12] mas/yr |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −3.62[11] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 14[11] M☉ |
| Age | 8[11] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Gamma Velorum is a quadruple star system in the constellation Vela. This name is the Bayer designation for the star, which is Latinised from γ Velorum and abbreviated γ Vel. At a combined magnitude of +1.72, it is one of the brightest stars in the night sky, and contains by far the closest and brightest Wolf–Rayet star. It has the traditional name Suhail al Muhlif and the modern name Regor /ˈriːɡɔːr/,[13] but neither is approved by the International Astronomical Union, making it the brightest star by apparent magnitude without an IAU approved name.
The γ Velorum system includes a pair of stars separated by 41″, each of which is also a spectroscopic binary system. γ2 Velorum, the brighter of the visible pair, contains the Wolf–Rayet star and a blue supergiant, while γ1 Velorum contains a blue giant and an unseen companion.
- ^ a b c d e van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600
- ^ a b c Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237: 0. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ^ a b Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007–2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1: 02025. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ^ Roche, P. F.; Colling, M. D.; Barlow, M. J. (2012). "The outer wind of γ Velorum". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 427 (1): 581. arXiv:1208.6016. Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..581R. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.22005.x. S2CID 119234167.
- ^ Niemela, V. S.; Sahade, J. (1980). "The orbital elements of Gamma 2 Velorum". The Astrophysical Journal. 238: 244. Bibcode:1980ApJ...238..244N. doi:10.1086/157981. ISSN 0004-637X.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Crowther, Paul A.; Barlow, M. J.; Royer, P.; Hillier, D. J.; Bestenlehner, J. M.; Morris, P. W.; Wesson, R. (2024-01-01). "Oxygen abundance of γ Vel from [O III] 88μm Herschel/PACS spectroscopy". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 528 (2): 2026. arXiv:2310.15170. Bibcode:2024MNRAS.528.2026C. doi:10.1093/mnras/stae145. ISSN 0035-8711.
- ^ Schmutz, W.; Schweickhardt, J.; Stahl, O.; Wolf, B.; Dumm, T.; Gang, Th.; Jankovics, I.; Kaufer, A.; Lehmann, H.; Mandel, H.; Peitz, J.; Rivinius, Th. (1997). "The orbital motion of gamma^2 Velorum". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 328: 219. Bibcode:1997A&A...328..219S.
- ^ a b c North, J. R.; Tuthill, P. G.; Tango, W. J.; Davis, J. (2007). "Γ2 Velorum: Orbital solution and fundamental parameter determination with SUSI". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 377 (1): 415–424. arXiv:astro-ph/0702375. Bibcode:2007MNRAS.377..415N. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11608.x. S2CID 16425744.
- ^ a b Hog, E.; Kuzmin, A.; Bastian, U.; Fabricius, C.; Kuimov, K.; Lindegren, L.; Makarov, V. V.; Roeser, S. (1998). "The TYCHO Reference Catalogue". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 335: L65. Bibcode:1998A&A...335L..65H.
- ^ a b c d Hernandez, C. A.; Sahade, J. (1980). "The Spectroscopic Binary GAMMA-1-VELORUM". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 92: 819. Bibcode:1980PASP...92..819H. doi:10.1086/130756. ISSN 0004-6280. S2CID 120181128.
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
jeffrieswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H. doi:10.1888/0333750888/2862.
- ^ Kunitzsch, Paul; Smart, Tim (2006). A Dictionary of Modern star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations (2nd rev. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Sky Pub. ISBN 978-1-931559-44-7.