| Part of a series on |
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
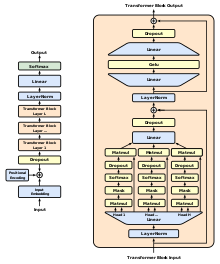
A generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) is a type of large language model (LLM)[1][2][3] and a prominent framework for generative artificial intelligence.[4][5] It is an artificial neural network that is used in natural language processing by machines.[6] It is based on the transformer deep learning architecture, pre-trained on large data sets of unlabeled text, and able to generate novel human-like content.[2][3] As of 2023, most LLMs had these characteristics[7] and are sometimes referred to broadly as GPTs.[8]
The first GPT was introduced in 2018 by OpenAI.[9] OpenAI has released significant GPT foundation models that have been sequentially numbered, to comprise its "GPT-n" series.[10] Each of these was significantly more capable than the previous, due to increased size (number of trainable parameters) and training. The most recent of these, GPT-4o, was released in May 2024.[11] Such models have been the basis for their more task-specific GPT systems, including models fine-tuned for instruction following—which in turn power the ChatGPT chatbot service.[1]
The term "GPT" is also used in the names and descriptions of such models developed by others. For example, other GPT foundation models include a series of models created by EleutherAI,[12] and seven models created by Cerebras in 2023.[13] Companies in different industries have developed task-specific GPTs in their respective fields, such as Salesforce's "EinsteinGPT" (for CRM)[14] and Bloomberg's "BloombergGPT" (for finance).[15]
- ^ a b Haddad, Mohammed. "How does GPT-4 work and how can you start using it in ChatGPT?". www.aljazeera.com.
- ^ a b "Generative AI: a game-changer society needs to be ready for". World Economic Forum. 9 January 2023.
- ^ a b "The A to Z of Artificial Intelligence". Time. April 13, 2023.
- ^ Hu, Luhui (November 15, 2022). "Generative AI and Future". Medium.
- ^ "CSDL | IEEE Computer Society". www.computer.org.
- ^ "LibGuides: Using AI Language Models : ChatGPT".
- ^ Toews, Rob. "The Next Generation Of Large Language Models". Forbes.
- ^ Mckendrick, Joe (March 13, 2023). "Most Jobs Soon To Be 'Influenced' By Artificial Intelligence, Research Out Of OpenAI And University Of Pennsylvania Suggests". Forbes.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
gpt1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "GPT-1 to GPT-4: Each of OpenAI's GPT Models Explained and Compared". MUO. April 11, 2023.
- ^ "GPT-4". openai.com. Retrieved 2023-12-08.
- ^ Alford, Anthony (July 13, 2021). "EleutherAI Open-Sources Six Billion Parameter GPT-3 Clone GPT-J". InfoQ.
- ^ "News" (Press release).
- ^ Morrison, Ryan (7 March 2023). "Salesforce launches EinsteinGPT built with OpenAI technology". Tech Monitor.
- ^ "The ChatGPT of Finance is Here, Bloomberg is Combining AI and Fintech". Forbes.