This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (September 2019) |
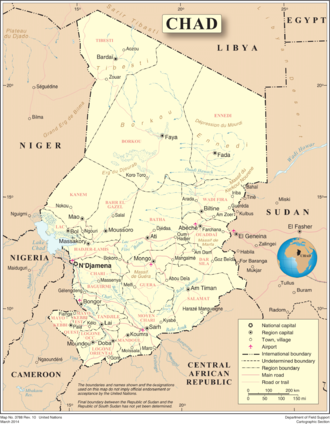

Chad is one of the 47 landlocked countries in the world and is located in North Central Africa, measuring 1,284,000 square kilometers (495,755 sq mi), nearly twice the size of France and slightly more than three times the size of California. Most of its ethnically and linguistically diverse population lives in the south, with densities ranging from 54 persons per square kilometer in the Logone River basin to 0.1 persons in the northern B.E.T. (Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti) desert region, which itself is larger than France. The capital city of N'Djaména, situated at the confluence of the Chari and Logone Rivers, is cosmopolitan in nature, with a current population in excess of 700,000 people.
Chad has four climatic zones. The northernmost Saharan zone averages less than 200 mm (7.9 in) of rainfall annually. The sparse human population is largely nomadic, with some livestock, mostly small ruminants and camels. The central Sahelian zone receives between 200 and 700 mm (7.9 and 27.6 in) rainfall and has vegetation ranging from grass/shrub steppe to thorny, open savanna. The southern zone, often referred to as the Sudan zone, receives between 700 and 1,000 mm (27.6 and 39.4 in), with woodland savanna and deciduous forests for vegetation. Rainfall in the Guinea zone, located in Chad's southwestern tip, ranges between 1,000 and 1,200 mm (39.4 and 47.2 in). In Chad forest cover is around 3% of the total land area, equivalent to 4,313,000 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, down from 6,730,000 hectares (ha) in 1990. In 2020, naturally regenerating forest covered 4,293,000 hectares (ha) and planted forest covered 19,800 hectares (ha). For the year 2015, 100% of the forest area was reported to be under public ownership.[1][2]
The country's topography is generally flat,[3] with the elevation gradually rising as one moves north and east away from Lake Chad. The highest point in Chad is Emi Koussi, a mountain that rises 3,100 m (10,171 ft) in the northern Tibesti Mountains. The Ennedi Plateau and the Ouaddaï highlands in the east complete the image of a gradually sloping basin, which descends towards Lake Chad. There are also central highlands in the Guera region rising to 1,500 m (4,921 ft).
Lake Chad is the second largest lake in west Africa[4] and is one of the most important wetlands on the continent.[5] Home to 120 species of fish and at least that many species of birds, the lake has shrunk dramatically in the last four decades due to increased water usage from an expanding population and low rainfall. Bordered by Chad, Niger, Nigeria, and Cameroon, Lake Chad currently covers only 1350 square kilometers, down from 25,000 square kilometers in 1963. The Chari and Logone Rivers, both of which originate in the Central African Republic and flow northward, provide most of the surface water entering Lake Chad. Chad is also next to Niger.
- ^ Terms and Definitions FRA 2025 Forest Resources Assessment, Working Paper 194. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023.
- ^ "Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Chad". Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Leonard 2005was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Mueckenheim, J.K. (2007). Countries of the World & Their Leaders Yearbook 08. Gale virtual reference library. Thomson Gale. p. 390. ISBN 978-0-7876-8107-4. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ "Lake Chad fishermen pack up their nets". BBC News. 15 January 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2019.