  | |
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Region | Horn of Africa |
| Area | Ranked 146th |
| • Total | 23,200 km2 (9,000 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 314 km (195 mi) |
| Borders | 575 km (357 mi) * * * * |
| Highest point | Mousa Ali 2,028 m (6,654 ft) |
| Lowest point | Lac Assal −155 m (−509 ft) |
| Largest lake | Lake Abbe |
| Terrain | Mostly mountainous and volcanic |
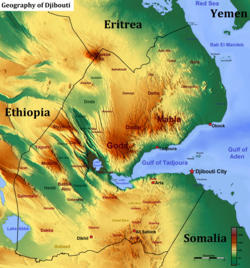
Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. To the east is its coastline on the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. Rainfall is sparse, and most of the territory has a semi-arid to arid environment. Lake Assal is a saline lake which lies 155 m (509 ft) below sea level, making it the lowest point on land in Africa and the third-lowest point on Earth after the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea. Djibouti has the fifth smallest population in Africa. Djibouti's major settlements include the capital Djibouti City, the port towns of Tadjoura and Obock, and the southern cities of Ali Sabieh and Dikhil. It is the forty-six country by area in Africa and 147st largest country in the world by land area, covering a total of 23,200 km2 (9,000 sq mi), of which 23,180 km2 (8,950 sq mi) is land and 20 km2 (7.7 sq mi) is water.[1]
- ^ "Djibouti". The World Factbook. CIA. April 16, 2015. Retrieved April 15, 2015.