 | |
| Continent | Europe and Asia |
|---|---|
| Region | Caucasus |
| Coordinates | 42°00′N 43°30′E / 42.000°N 43.500°E |
| Area | Ranked 119 |
| • Total | 69,700 km2 (26,900 sq mi) |
| • Land | 100% |
| • Water | 0% |
| Coastline | 310 km (190 mi) |
| Borders | 1,814 km (1,127 mi)
|
| Highest point | Mount Shkhara 5,201 m (17,064 ft) |
| Lowest point | Between Poti and Kulevi, (-1.5-2.3 m)[1] |
| Longest river | Alazani River 407 km (253 mi) |
| Largest lake | Paravani Lake, 37.5 km2 (14.5 sq mi) |
| Climate | Temperate to subtropical |
| Terrain | Mountainous with a coastal plain |
| Natural resources | timber, hydropower, manganese deposits, iron ore, copper, minor coal and petroleum deposits; coastal climate and soils allow for important tea and citrus growth |
| Natural hazards | earthquakes |
| Environmental issues | air and water pollution, soil pollution from toxic chemicals |
| Exclusive economic zone | 21,946 km2 (8,473 sq mi) |
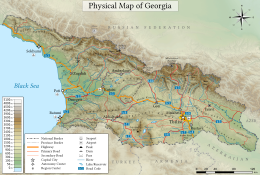
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region on the coast of the Black Sea. Sometimes considered a transcontinental country, it is located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia,[2] and is today generally regarded as part of Europe.[3][4][5][6] It is bordered to the north and northeast by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan.[7]
- ^ Geography of Georgia - 9th grade book; G. Chanturia, D. Kereselidze; p. 43
- ^ "Caucasus - region and mountains, Eurasia". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 26 November 2018. Quote: “One widely accepted scheme draws the dividing line along the crest of the Greater Caucasus range, putting the portion of the region north of the line in Europe...another scheme identifies the Aras River and the Turkish border as the line of continental demarcation, thereby locating...Georgia in Europe.”
- ^ International Geographic Encyclopaedia and Atlas. Springer: p. 273
- ^ Encyclopedic World Atlas, George Philip & Son, Oxford University Press: 2002, p.104
- ^ "Georgia - 46 States, one Europe". Council of Europe. Retrieved 2023-08-12.
- ^ "Europe - Georgia". World Health Organization. Retrieved 2023-08-12.
- ^ Nana Bolashvili, Andreas Dittmann, Lorenz King, Vazha Neidze (eds.): National Atlas of Georgia, 138 pages, Steiner Verlag, 2018, ISBN 978-3-515-12057-9