Native name: Kalaallit Nunaat Grønland Greenland | |
|---|---|
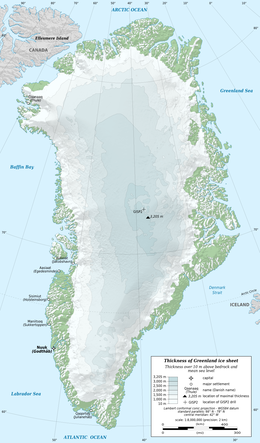 Outline map of Greenland with ice sheet depths. (Much of the area in green has permanent snow cover, but less than 10m (33ft) thick.) | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean |
| Coordinates | 64°10′N 51°43′W / 64.167°N 51.717°W |
| Area | 2,166,086 km2 (836,330 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 1st |
| Coastline | 44,087 km (27394.4 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 3,694 m (12119 ft) |
| Highest point | Gunnbjørn |
| Administration | |
| Province | |
| Largest settlement | Nuuk (Godthåb) (pop. 17,984) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 56,732 (February 8, 2020) |
| Pop. density | 0.028/km2 (0.073/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | |
Greenland is located between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Canada and northwest of Iceland. The territory comprises the island of Greenland—the largest island in the world—and more than a hundred other smaller islands (see alphabetic list). Greenland has a 1.2-kilometer-long (0.75 mi) border with Canada on Hans Island.[1] A sparse population is confined to small settlements along certain sectors of the coast. Greenland possesses the world's second-largest ice sheet.
Greenland sits atop the Greenland plate, a subplate of the North American Plate.[2][3] The Greenland craton is made up of some of the oldest rocks on the face of the earth. The Isua greenstone belt in southwestern Greenland contains the oldest known rocks on Earth, dated at 3.7–3.8 billion years old.[4]
The vegetation is generally sparse, with the only patch of forested land being found in Nanortalik Municipality in the extreme south near Cape Farewell.
The climate is arctic to subarctic, with cool summers and cold winters. The terrain is mostly a flat but gradually sloping icecap that covers all land except for a narrow, mountainous, barren, rocky coast. The lowest elevation is sea level and the highest elevation is the summit of Gunnbjørn Fjeld, the highest point in the Arctic at 3,694 meters (12,119 ft). The northernmost point of the island of Greenland is Cape Morris Jesup, discovered by Admiral Robert Peary in 1900. Natural resources include zinc, lead, iron ore, coal, molybdenum, gold, platinum, uranium, hydropower and fish.
- ^ "On tiny Hans Island, Denmark and Canada create world's newest land border". Big Think. 2022-06-14. Retrieved 2023-07-07.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- ^ "Baffin Bay" (PDF). Indian and Northern Affairs Canada. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-13. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- ^ Appel, Peter W.U., Hugh R. Rollinson, and Jacques L.R. Touret. (2001) "Remnants of an Early Archaean (>3.75 Ga) sea-floor, hydrothermal system in the Isua Greenstone Belt." Precambrian Research, 112.1–2, 15 November, pp. 27–49.