 | |
| Continent | Asia |
|---|---|
| Region | Middle East |
| Coordinates | 25°18′N 51°09′E / 25.30°N 51.15°E |
| Area | Ranked 164th |
| • Total | 11,571 km2 (4,468 sq mi) |
| • Land | 100% |
| • Water | 0% |
| Coastline | 563 km (350 mi) |
| Borders | Saudi Arabia: 60 km (37 mi) |
| Highest point | Qurayn Abu al Bawl, 103 m (338 ft) |
| Lowest point | Dukhan Sabkha, −7 m (−23 ft) |
| Climate | arid; mild, pleasant winters; very hot, humid summers |
| Terrain | mostly flat and barren desert covered with loose sand and gravel |
| Natural resources | petroleum, natural gas, fish |
| Natural hazards | haze, dust storms, sandstorms common |
| Environmental issues | limited natural freshwater resources are increasing dependence on large-scale desalination facilities |
| Exclusive economic zone | 31,590 km2 (12,197 sq mi) |

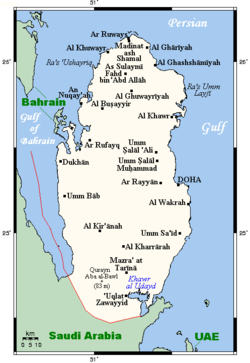
Qatar is a peninsula in the east of Arabia, bordering the Persian Gulf and Saudi Arabia, in a strategic location near major petroleum and natural gas deposits. The State of Qatar occupies 11,571 km2 (4,468 sq mi) on a peninsula that extends approximately to 160 km (99 mi) north into the Persian Gulf from the Arabian Peninsula.[1]
Varying in width between 55 and 90 km (34 and 56 mi), the land is mainly flat (the highest point is 103 m (338 ft)) and rocky.[1] Notable features include coastal salt pans, elevated limestone formations (the Dukhan anticline) along the west coast under which lies the Dukhan oil field, and massive sand dunes surrounding Khor Al Adaid, an inlet of the Persian Gulf in the southeast known to local English speakers as the Inland Sea.[1]
- ^ a b c Toth, Anthony (1994). "Qatar: Geography". In Metz, Helen Chapin (ed.). Persian Gulf states: country studies (3rd ed.). Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 162–163. ISBN 0-8444-0793-3. OCLC 29548413.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.