| Glaucophyta | |
|---|---|
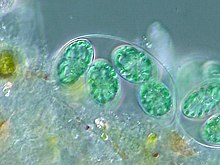
| |
| Glaucocystis sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Clade: | Archaeplastida |
| Division: | Glaucophyta Skuja 1948 |
| Class | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments,[1][2] less common today than they were during the Proterozoic.[3] The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26.[4][5][6] Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants (Viridiplantae or Chloroplastida), they form the Archaeplastida.
The glaucophytes are of interest to biologists studying the evolution of chloroplasts as they may be similar to the original algal type that led to the red algae and green plants, i.e. glaucophytes may be basal Archaeplastida.[1][7][4]
Unlike red and green algae, glaucophytes only have asexual reproduction.[8]
- ^ a b Keeling, Patrick J. (2004). "Diversity and evolutionary history of plastids and their hosts". American Journal of Botany. 91 (10): 1481–1493. doi:10.3732/ajb.91.10.1481. PMID 21652304.
- ^ Genomic Insights Into the Biology of Algae
- ^ Cruzan, Mitchell B. (2018). Evolutionary Biology. Oxford University Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-19-088268-6.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
FiguJackReye19was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ The monoplastidic bottleneck in algae and plant evolution | Journal of Cell Science
- ^ Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. "Glaucophyta". AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ Kim, Eunsoo; Graham, Linda E. (2008). Redfield, Rosemary Jeanne (ed.). "EEF2 Analysis Challenges the Monophyly of Archaeplastida and Chromalveolata". PLoS ONE. 3 (7): e2621. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.2621K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002621. PMC 2440802. PMID 18612431.
- ^ Walker, Timothy (2012). Plants: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-19-958406-2.