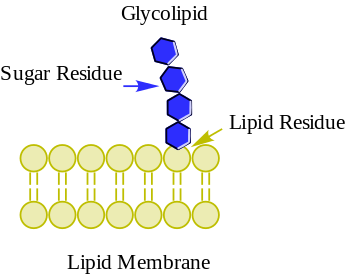
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond.[1] Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues.[2] Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment.[2]
- ^ Voet D, Voet J, Pratt C (2013). Fundamentals of Biochemistry Life at the Molecular Level (Fourth ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 9781118129180.
- ^ a b "Glycolipids". nature. Nature Publishing Group. Retrieved 1 November 2015.