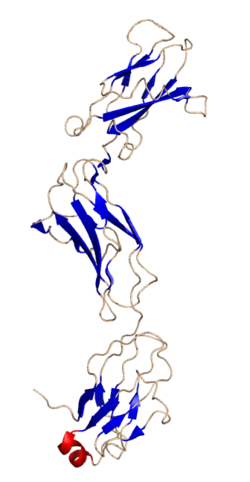
Glycoprotein 130 (also known as gp130, IL6ST, IL6R-beta or CD130) is a transmembrane protein which is the founding member of the class of tall cytokine receptors. It forms one subunit of the type I cytokine receptor within the IL-6 receptor family. It is often referred to as the common gp130 subunit, and is important for signal transduction following cytokine engagement. As with other type I cytokine receptors, gp130 possesses a WSXWS amino acid motif that ensures correct protein folding and ligand binding. It interacts with Janus kinases to elicit an intracellular signal following receptor interaction with its ligand. Structurally, gp130 is composed of five fibronectin type-III domains and one immunoglobulin-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain in its extracellular portion.[5][6]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000134352 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021756 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Hibi M, Murakami M, Saito M, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1990). "Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130". Cell. 63 (6): 1149–1157. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. PMID 2261637. S2CID 30852638.
- ^ Bravo J, Staunton D, Heath JK, Jones EY (1998). "Crystal structure of a cytokine-binding region of gp130". EMBO J. 17 (6): 1665–1674. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.6.1665. PMC 1170514. PMID 9501088.