
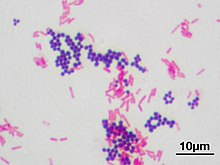
Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. It may also be used to diagnose a fungal infection.[1] The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique in 1884.[2]
Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls. Gram-positive cells have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in the cell wall that retains the primary stain, crystal violet. Gram-negative cells have a thinner peptidoglycan layer that allows the crystal violet to wash out on addition of ethanol. They are stained pink or red by the counterstain,[3] commonly safranin or fuchsine. Lugol's iodine solution is always added after addition of crystal violet to form a stable complex with crystal violet that strengthen the bonds of the stain with the cell wall.[4]
Gram staining is almost always the first step in the identification of a bacterial group. While Gram staining is a valuable diagnostic tool in both clinical and research settings, not all bacteria can be definitively classified by this technique. This gives rise to gram-variable and gram-indeterminate groups.
- ^ "Gram Stain: MedlinePlus Medical Test". medlineplus.gov.
- ^ Colco, R. (2005). "Gram Staining". Current Protocols in Microbiology. Appendix 3 (1): Appendix 3C. doi:10.1002/9780471729259.mca03cs00. ISBN 978-0471729259. PMID 18770544. S2CID 32452815.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Beveridge_and_Davies_1983was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Libenson, L.; McIlroy, A. P. (1955-07-01). "On the Mechanism of the Gram Stain". Journal of Infectious Diseases. 97 (1): 22–26. doi:10.1093/infdis/97.1.22. ISSN 0022-1899.