This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2022) |
| Part of a series on |
| Astrodynamics |
|---|
A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby which makes use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense.
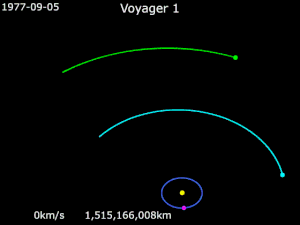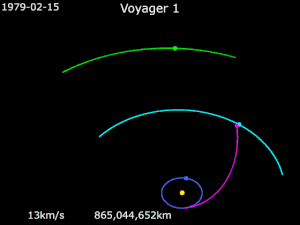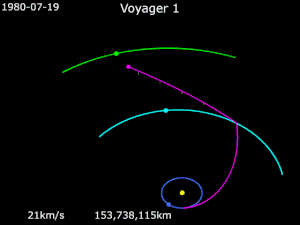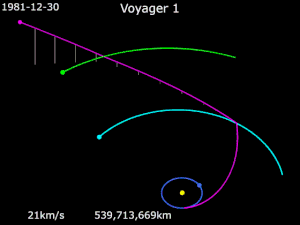
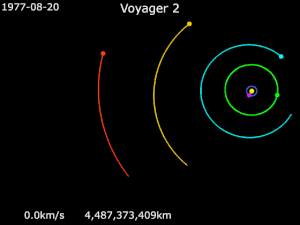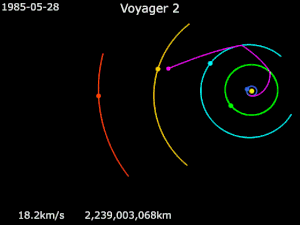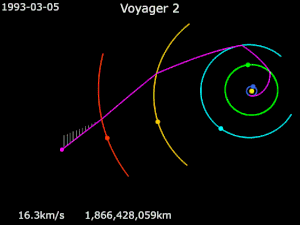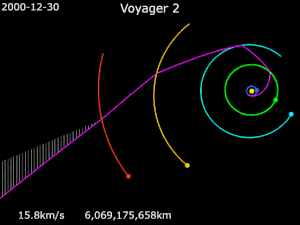
Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft.[1] Any gain or loss of kinetic energy and linear momentum by a passing spacecraft is correspondingly lost or gained by the gravitational body, in accordance with Newton's Third Law. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon, and it was used by interplanetary probes from Mariner 10 onward, including the two Voyager probes' notable flybys of Jupiter and Saturn.
- ^ "Section 1: Environment, Chapter 4: Trajectories". Basics of Space Flight. NASA. Retrieved 21 July 2018.