| Gregarinasina | |
|---|---|
| |
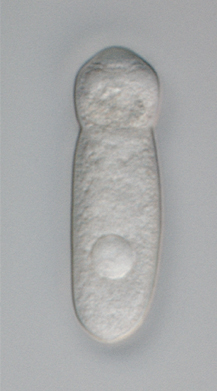
| A live specimen of a septate (or cephaline) gregarine showing the distinctive "head"-like section of the trophozoite containing the epimerite at its anterior end. Septate gregarines are intestinal parasites of arthropods. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Apicomplexa |
| Class: | Conoidasida |
| Subclass: | Gregarinasina |
| Orders | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina[1] or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. Gregarines are closely related to both Toxoplasma and Plasmodium, which cause toxoplasmosis and malaria, respectively. Both protists use protein complexes similar to those that are formed by the gregarines for gliding motility and for invading target cells.[2][3] This makes the gregarines excellent models for studying gliding motility, with the goal of developing treatment options for both toxoplasmosis and malaria. Thousands of different species of gregarine are expected to be found in insects, and 99% of these gregarine species still need to be described. Each insect species can be the host of multiple gregarine species.[4][5] One of the most-studied gregarines is Gregarina garnhami. In general, gregarines are regarded as a very successful group of parasites, as their hosts are distributed over the entire planet.[6]
- ^ Carreno RA, Martin DS, Barta JR (November 1999). "Cryptosporidium is more closely related to the gregarines than to coccidia as shown by phylogenetic analysis of apicomplexan parasites inferred using small-subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences". Parasitol. Res. 85 (11): 899–904. doi:10.1007/s004360050655. PMID 10540950. Archived from the original on 2001-03-20.
- ^ Ménard R (February 2001). "Gliding motility and cell invasion by Apicomplexa: insights from the Plasmodium sporozoite". Cell. Microbiol. 3 (2): 63–73. doi:10.1046/j.1462-5822.2001.00097.x. PMID 11207621.
- ^ Meissner M, Schlüter D, Soldati D (October 2002). "Role of Toxoplasma gondii myosin A in powering parasite gliding and host cell invasion". Science. 298 (5594): 837–40. Bibcode:2002Sci...298..837M. doi:10.1126/science.1074553. PMID 12399593.
- ^ Valigurová, Andrea; Koudela, Břetislav (August 2008). "Morphological analysis of the cellular interactions between the eugregarine Gregarina garnhami (Apicomplexa) and the epithelium of its host, the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria". European Journal of Protistology. 44 (3): 197–207. doi:10.1016/j.ejop.2007.11.006. PMID 18304787.
- ^ Lange, C.E.; Lord, J.C. (2012). Insect Pathology - 2nd Edition (2nd ed.). Elsevier/Academic Press. pp. 367–387. ISBN 9780123849847.
- ^ Cox, FE (December 1994). "The evolutionary expansion of the Sporozoa". International Journal for Parasitology. 24 (8): 1301–16. doi:10.1016/0020-7519(94)90197-x. PMID 7729983.