This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Wytensin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a686003 |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Elimination half-life | 6 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.410 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
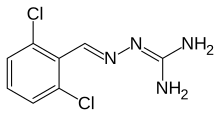
| Formula | C8H8Cl2N4 |
| Molar mass | 231.08 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Guanabenz (pronounced GWAHN-a-benz, sold under the trade name Wytensin) is an alpha agonist that is selective to the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor. Guanabenz is used as an antihypertensive drug used in the treatment of high blood pressure (hypertension).[1][2]
The most common side effects during guanabenz therapy are dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, headache and weakness.[3]
Guanabenz can make one drowsy or less alert, therefore driving or operating dangerous machinery is not recommended.
- ^ Walker BR, Hare LE, Deitch MW (1982). "Comparative antihypertensive effects of guanabenz and clonidine". The Journal of International Medical Research. 10 (1): 6–14. doi:10.1177/030006058201000102. PMID 7037502. S2CID 2139809.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Bonham AC, Trapani AJ, Portis LR, Brody MJ (December 1984). "Studies on the mechanism of the central antihypertensive effect of guanabenz and clonidine". Journal of Hypertension Supplement. 2 (3): S543–S546. PMID 6599714.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Guanabenz | The Merck Index Online". www.rsc.org. Retrieved 2023-04-17.