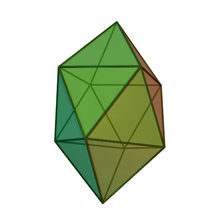
| Gyroelongated square bipyramid | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Gyroelongated bipyramid, Deltahedron, Johnson J16 – J17 – J18 |
| Faces | 16 triangles |
| Edges | 24 |
| Vertices | 10 |
| Vertex configuration | |
| Symmetry group | |
| Dual polyhedron | Truncated square trapezohedron |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |
In geometry, the gyroelongated square bipyramid is a polyhedron with 16 triangular faces. it can be constructed from a square antiprism by attaching two equilateral square pyramids to each of its square faces. The same shape is also called hexakaidecadeltahedron[1], heccaidecadeltahedron,[2] or tetrakis square antiprism;[1] these last names mean a polyhedron with 16 triangular faces. It is an example of deltahedron, and of a Johnson solid.
The dual polyhedron of the gyroelongated square bipyramid is a square truncated trapezohedron with eight pentagons and two squares as its faces. The gyroelongated square pyramid appears in chemistry as the basis for the bicapped square antiprismatic molecular geometry, and in mathematical optimization as a solution to the Thomson problem.

