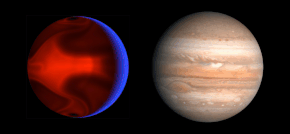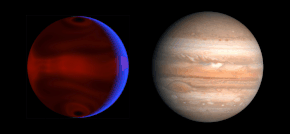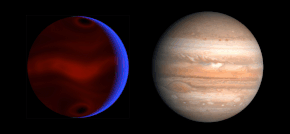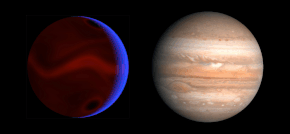
 Computer simulation of weather systems on HD 80606 b, to scale with Jupiter | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Geneva Extrasolar Planet Search |
| Discovery site | Haute-Provence Observatory |
| Discovery date | 4 April 2001[2] |
| Radial velocity | |
| Orbital characteristics[3] | |
| Apastron | 0.8821 AU (131,960,000 km) |
| Periastron | 0.0309 AU (4,620,000 km) |
| 0.4565 ± 0.0053 AU (68,290,000 ± 790,000 km) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.93226+0.00064 −0.00069 |
| 111.43670±0.00040 d | |
Average orbital speed | 8.8 km/s – 47.3 km/s[notes 1] |
| Inclination | 89.232°±0.029° |
| 2,454,424.857 ± 0.05[4] | |
| 301.03°+0.20° −0.19° | |
| Semi-amplitude | 474.9+2.5 −2.7 m/s |
| Star | HD 80606 |
| Physical characteristics[3] | |
| 1.003±0.023 RJ | |
| Mass | 4.116+0.097 −0.100 MJ |
Mean density | 5.06+0.38 −0.35 g/cm3 |
| 9.6 g | |
| 93+85 −35 h[5] | |
| Temperature | <500 - 1400 K[5] |
HD 80606 b (also Struve 1341 Bb or HIP 45982 b) is an eccentric hot Jupiter 217 light-years from the Sun in the constellation of Ursa Major. HD 80606 b was discovered orbiting the star HD 80606 in April 2001 by a team led by Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz.[2] With a mass 4 times that of Jupiter, it is a gas giant. Because the planet transits the host star its radius can be determined using the transit method, and was found to be about the same as Jupiter's. Its density is slightly less than Earth's.[6] It has an extremely eccentric orbit like a comet, with its orbit taking it very close to its star and then back out very far away from it every 111 days.[7]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Naef2001was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
eso0114was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Bonomo2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
moutou2009was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
deWit2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
fossey2009was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Investigating the Mystery of Migrating 'Hot Jupiters'". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. 28 March 2016. Archived from the original on 24 March 2023.
Cite error: There are <ref group=notes> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=notes}} template (see the help page).