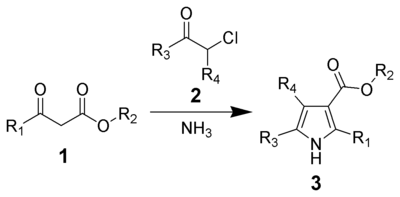
The Hantzsch Pyrrole Synthesis, named for Arthur Rudolf Hantzsch, is the chemical reaction of β-ketoesters (1) with ammonia (or primary amines) and α-haloketones (2) to give substituted pyrroles (3).[1][2] Pyrroles are found in a variety of natural products with biological activity, so the synthesis of substituted pyrroles has important applications in medicinal chemistry.[3][4] Alternative methods for synthesizing pyrroles exist, such as the Knorr Pyrrole Synthesis and Paal-Knorr Synthesis.
- ^ Hantzsch, A. Ber. 1890, 23, 1474.
- ^ Feist, F. Ber. 1902, 35, 1538.
- ^ Furstner, A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42¸ 3582-3603.
- ^ Leonardi, Marco; Estévez, Verónica; Villacampa, Mercedes; Menéndez, J. (February 2019). "The Hantzsch Pyrrole Synthesis: Non-conventional Variations and Applications of a Neglected Classical Reaction". Synthesis. 51 (4): 816–828. doi:10.1055/s-0037-1610320. ISSN 0039-7881. S2CID 104444238.