This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (April 2018) |
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (June 2024) |
| Harar Governorate Governatorato di Harar | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governorate of Italian East Africa | |||||||||
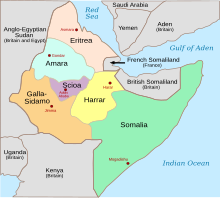 Harar (yellow) within Italian East Africa | |||||||||
| Capital | Harar | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• | ca. 1,600,000 | ||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||
• 1936-1939 | Guglielmo Nasi | ||||||||
• 1939-1940 | Enrico Cerulli | ||||||||
• 1940-1941 | Guglielmo Nasi | ||||||||
• 1941 | Pompeo Gorini | ||||||||
• 1941 | Carlo De Simone | ||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period World War II | ||||||||
• Created | 1 June 1936 | ||||||||
| 24 April 1941 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
Harar Governorate was one of the six governorates of Italian East Africa. It was formed in 1936 from parts of the conquered Ethiopian Empire following the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
The capital of governorate was Harar, but Dire Dawa was the most important city. In the territories around these two cities more than 10,000 Italian colonists went to live since 1937 creating some manufacturing industries (after the area was pacified from the Arbegnoch guerrilla). In November 1938 some territory of Harar in the Scioa region was given to the neighboring Addis Abeba Governorate, enlarging it to the Scioa Governorate.

The Harar governorate was subdivided in the "Commissariati" of Arussi, Cercer, Dire Dawa, Ghimir, Giggiga, Goba, Harar and Adama.
