 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈhɛpərɪn/ HEP-ər-in |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous therapy, subcutaneous injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Erratic |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion | Urine[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.698 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
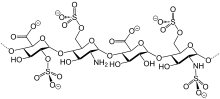
| Formula | C12H19NO20S3 |
| Molar mass | 593.45 g·mol−1 |
| |
| | |
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan.[3][4] Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin.[5] It is used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina.[3] It can be given intravenously or by injection under the skin.[3] Its anticoagulant properties make it useful to prevent blood clotting in blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines.[4][6]
Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets.[3] Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.[3] Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function.[3]
Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4/heparin complex autoimmune manner, in favor of alternative anticoagulant medications (such as argatroban or danaparoid).[7][8][9]
Heparin appears to be relatively safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.[10] Heparin is produced by basophils and mast cells in all mammals.[11]
The discovery of heparin was announced in 1916.[12] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[13] A fractionated version of heparin, known as low molecular weight heparin, is also available.[14]
- ^ a b "Heparin Interpharma APMDS". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 7 December 2023. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- ^ "Heparin". 10 February 2012. Archived from the original on 14 February 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f "Heparin Sodium". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- ^ a b "Heparin (Mucous) Injection BP – Summary of Product Characteristics". Electronic Medicines Compendium. September 2016. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ^ Alquwaizani M, Buckley L, Adams C, Fanikos J (June 2013). "Anticoagulants: A Review of the Pharmacology, Dosing, and Complications". Current Emergency and Hospital Medicine Reports. 1 (2): 83–97. doi:10.1007/s40138-013-0014-6. PMC 3654192. PMID 23687625.
- ^ McClatchey KD (2002). Clinical Laboratory Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 662. ISBN 978-0-683-30751-1. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
- ^ "AstraZeneca COVID-19-Vakzine Umgang mit dem Risiko von Gerinnungskomplikationen" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 January 2024. Retrieved 3 April 2021.
- ^ Greinacher A, Thiele T, Warkentin TE, Weisser K, Kyrle PA, Eichinger S (June 2021). "Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination". The New England Journal of Medicine. 384 (22): 2092–2101. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2104840. PMC 8095372. PMID 33835769.
- ^ Pai M, Grill A, Ivers N (26 March 2021). "Vaccine-Induced Prothrombotic Immune Thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) Following AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccination" (PDF). The Ontario COVID-19 Science Advisory Table. doi:10.47326/ocsat.2021.02.17.1.0. S2CID 233663558. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 March 2021. Retrieved 3 April 2021.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Heparin Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ^ Guyton AC, Hall JE (2006). Textbook of Medical Physiology. Elsevier Saunders. p. 464. ISBN 978-0-7216-0240-0.
- ^ Li JL, Corey EJ (2013). Drug Discovery: Practices, Processes, and Perspectives. John Wiley & Sons. p. 189. ISBN 978-1-118-35446-9. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ Rietschel RL, Fowler JF, Fisher AA (2008). Fisher's Contact Dermatitis. PMPH-USA. p. 142. ISBN 978-1-55009-378-0. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.