| Constellation | |
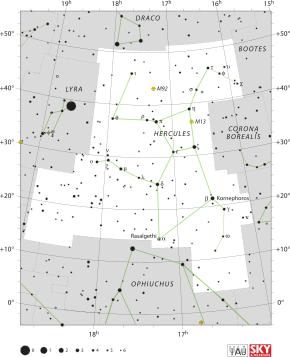 | |
| Abbreviation | Her |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Herculis[1] |
| Pronunciation | /ˈhɜːrkjʊliːz/, genitive /ˈhɜːrkjʊlɪs/ |
| Symbolism | Heracles |
| Right ascension | 17h |
| Declination | +30° |
| Quadrant | NQ3 |
| Area | 1225 sq. deg. (5th) |
| Main stars | 14, 22 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 106 |
| Stars with planets | 15 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 2 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 9 |
| Brightest star | β Her (Kornephoros) (2.78m) |
| Messier objects | 2 |
| Meteor showers | Tau Herculids |
| Bordering constellations | Draco Boötes Corona Borealis Serpens Caput Ophiuchus Aquila Sagitta Vulpecula Lyra[1] |
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −50°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of July. | |
Hercules is a constellation named after Hercules, the Roman mythological hero adapted from the Greek hero Heracles. Hercules was one of the 48 constellations listed by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is the fifth-largest of the modern constellations and is the largest of the 50 which have no stars brighter than apparent magnitude +2.5.