| Hesperocyparis guadalupensis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Cupressales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Hesperocyparis |
| Species: | H. guadalupensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hesperocyparis guadalupensis (S.Watson) Bartel
| |

| |
| Natural range | |
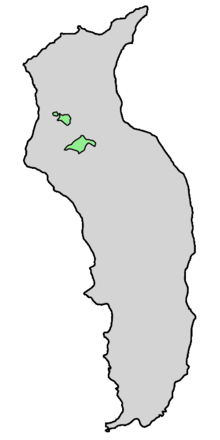
| |
| Guadalupe Island | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Hesperocyparis guadalupensis, commonly known as Guadalupe cypress, is a species of western cypress from Guadalupe Island in the Pacific Ocean off the western coast of Mexico's Baja Peninsula. It was previously known as Cupressus guadalupensis until 2009. It is a medium-sized tree with fine green to blue-green foliage. In its native habitat it depends on water from the fogs that envelop high ground in the northern half of the island. It became an endangered species due to feral goats living on Guadalupe Island that – for more than a century – prevented new trees from growing. In 2005 the goats were finally removed from the tree's island home as part of an island restoration project. New trees are growing and other plants are beginning to recover, though the future of the species is not yet assured. Guadalupe cypress is closely related to the vulnerable Tecate cypress, which grows on the mainland in Baja California and southern California. It is used as an ornamental tree in Mediterranean climates, particularly in Europe, but has no other significant human uses.
- ^ Farjon, A. (2013). "Cupressus guadalupensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2013: e.T42220A2962608. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42220A2962608.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ "Hesperocyparis guadalupensis (S.Watson) Bartel". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 16 February 2024.
