| HindIII restriction endonuclease | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | RE_Hindiii | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09518 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR019043 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| hindIIIR type II restriction endonuclease | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | hindIIIR | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 950303 | ||||||
| PDB | 2e52 More structures | ||||||
| UniProt | P43870 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| EC number | 3.1.21.4 | ||||||
| |||||||
HindIII (pronounced "Hin D Three") is a type II site-specific deoxyribonuclease restriction enzyme isolated from Haemophilus influenzae that cleaves the DNA palindromic sequence AAGCTT in the presence of the cofactor Mg2+ via hydrolysis.[1]
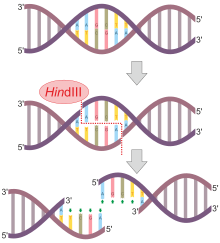
The cleavage of this sequence between the AA's results in 5' overhangs on the DNA called sticky ends:
5'-A |A G C T T-3'
3'-T T C G A| A-5'
Restriction endonucleases are used as defense mechanisms in prokaryotic organisms in the restriction modification system. Their primary function is to protect the host genome against invasion by foreign DNA, primarily bacteriophage DNA. There is also evidence that suggests the restriction enzymes may act alongside modification enzymes as selfish elements, or may be involved in genetic recombination and transposition.[2]
- ^ Tang, D; et al. (2000). "Mutational analyses of restriction endonuclease-HindIII mutant E86K with higher activity and altered specificity". Protein Engineering. 13 (4): 283–9. doi:10.1093/protein/13.4.283. PMID 10810160.
- ^ Pingoud, Alfred; Jeltsch, Albert. (2001). "Structure and function of type II restriction endonucleases". Nucleic Acids Research. 29 (18): 3705–27. doi:10.1093/nar/29.18.3705. PMC 55916. PMID 11557805.