| Part of a series on the |
| History of Assam |
|---|
 |
| Categories |
| History of South Asia |
|---|
 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Assam |
|---|
 |
The history of Assam is the history of a confluence of people from the east, west, south and the north; the confluence of the Austroasiatic, Tibeto-Burman (Sino-Tibetan), Tai and Indo-Aryan cultures. Although invaded over the centuries, it was never a vassal or a colony to an external power until the third Burmese invasion in 1821, and, subsequently, the British ingress into Assam in 1824 during the First Anglo-Burmese War.
The Assamese history has been derived from multiple sources. The Ahom kingdom of medieval Assam maintained chronicles, called Buranjis, written in the Ahom and the Assamese languages. History of ancient Assam comes from a corpus of Kamarupa inscriptions on rock, copper plates, clay; royal grants, etc. that the Kamarupa kings issued during their reign. Evidence about the cultural history and socio-religious beliefs of the people of the region can also be derived from the Kalika Purana and the Yogini Tantra, both believed to be composed in this region around the early medieval and medieval times. The religious literature of the Neo-Vaishnavite movement introduced by Sankaradeva are other important primary sources for the region's history.
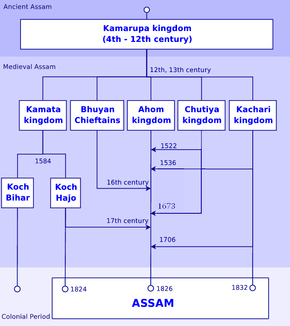
The history of Assam can be divided into four eras. The ancient era began in the 4th century with the mention of Kamarupa in Samudragupta's inscriptions on the Allahabad pillar and the establishment of the Kamarupa kingdom. The medieval era began with the attacks from the Bengal Sultanate, the first of which took place in 1206 by Bakhtiyar Khilji as mentioned in the Kanai-boroxiboa rock inscription, after the breakup of the ancient kingdom and the sprouting of medieval kingdoms and chieftain-ships in its place. The colonial era began with the establishment of British control after the Treaty of Yandaboo in 1826, and the post-colonial era began in 1947 after the Independence of India.
A common theme of Medieval kingship narratives in Assam is associated with shaktism and the Kamakhya temple.[5]
- ^ Baruah 1986.
- ^ "639 Identifier Documentation: aho – ISO 639-3". SIL International (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics). SIL International. Retrieved 2019-06-29.
Ahom [aho]
- ^ "Population by Religious Communities". Census India – 2001. Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. Retrieved 2019-07-01.
Census Data Finder/C Series/Population by Religious Communities
- ^ "Population by religion community – 2011". Census of India, 2011. The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 25 August 2015.
2011census/C-01/DDW00C-01 MDDS.XLS
- ^ (Urban 2009:86)