 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | HupA |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 10-14h[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.430 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
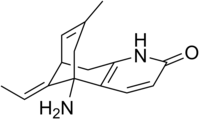
| Formula | C15H18N2O |
| Molar mass | 242.322 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 217 to 219 °C (423 to 426 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Huperzine A is a naturally-occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid compound found in the firmoss Huperzia serrata[2] and in varying quantities in other food Huperzia species, including H. elmeri, H. carinat, and H. aqualupian.[3] Huperzine A has been investigated as a treatment for neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, but a 2013 meta-analysis of those studies concluded that they were of poor methodological quality and the findings should be interpreted with caution.[4][5] Huperzine A inhibits the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. It is also an antagonist of the NMDA-receptor. It is commonly available over the counter as a nutritional supplement and marketed as a memory and concentration enhancer.
Huperzine A has also been noted to help induce lucid dreaming.[6]
- ^ Li YX, Zhang RQ, Li CR, Jiang XH (2007). "Pharmacokinetics of huperzine A following oral administration to human volunteers". European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 32 (4): 183–187. doi:10.1007/BF03191002. PMID 18348466. S2CID 2702029.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Zangara2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Lim WH, Goodger JQ, Field AR, Holtum JA, Woodrow IE (September 2010). "Huperzine alkaloids from Australasian and southeast Asian Huperzia". Pharmaceutical Biology. 48 (9): 1073–1078. doi:10.3109/13880209.2010.485619. PMID 20731560.
- ^ Yang G, Wang Y, Tian J, Liu JP (2013). "Huperzine A for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials". PLOS ONE. 8 (9): e74916. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...874916Y. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074916. PMC 3781107. PMID 24086396.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
cochranemetawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Lucid Dreaming: A Beginner's Guide". The Four Hour Work Week. Retrieved 29 December 2016.