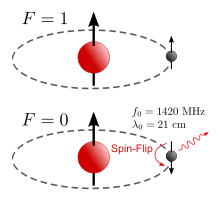
The hydrogen line, 21 centimeter line, or H I line[a] is a spectral line that is created by a change in the energy state of solitary, electrically neutral hydrogen atoms. It is produced by a spin-flip transition, which means the direction of the electron's spin is reversed relative to the spin of the proton. This is a quantum state change between the two hyperfine levels of the hydrogen 1 s ground state. The electromagnetic radiation producing this line has a frequency of 1420.405751768(2) MHz (1.42 GHz),[1] which is equivalent to a wavelength of 21.106114054160(30) cm in a vacuum. According to the Planck–Einstein relation E = hν, the photon emitted by this transition has an energy of 5.8743261841116(81) μeV [9.411708152678(13)×10−25 J]. The constant of proportionality, h, is known as the Planck constant.
The hydrogen line frequency lies in the L band, which is located in the lower end of the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. It is frequently observed in radio astronomy because those radio waves can penetrate the large clouds of interstellar cosmic dust that are opaque to visible light. The existence of this line was predicted by Dutch astronomer H. van de Hulst in 1944, then directly observed by E. M. Purcell and his student H. E. Ewen in 1951. Observations of the hydrogen line have been used to reveal the spiral shape of the Milky Way, to calculate the mass and dynamics of individual galaxies, and to test for changes to the fine-structure constant over time. It is of particular importance to cosmology because it can be used to study the early Universe. Due to its fundamental properties, this line is of interest in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. This line is the theoretical basis of the hydrogen maser.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Hellwig, Helmut; et al. (1970). "Measurement of the unperturbed hydrogen hyperfine transition frequency" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement. IM-19 (4): 200. Bibcode:1970ITIM...19..200H. doi:10.1109/TIM.1970.4313902. Retrieved 2023-04-30.