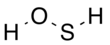| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sulfenic acid
| |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Thioperoxol | |||
| Other names
Sulfenic acid
oxadisulfane Sulfur hydride hydroxide Sulfonol Sulfanol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| 672 | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2OS | |||
| Molar mass | 50.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.249 | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.484 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Hydrogen thioperoxide, also called oxadisulfane or sulfanol, is the chemical with the structure H–S–O–H. It can be considered as the simple sulfur-substituted analog of the common hydrogen peroxide (H–O–O–H) chemical, and as the simplest hydrogen chalcogenide containing more than one type of chalcogen. The chemical has been described as the "missing link" between hydrogen peroxide and hydrogen disulfide (H–S–S–H),[2] though it is substantially less stable than either of the other two. It is the inorganic parent structure of the sulfenic acid class of organic compounds (R–S–O–H) and also the oxadisulfide linkage (R1–S–O–R2), where "R" is any organic structure. Sulfur is present in oxidation state 0.
- ^ Iraqi, Muhammad; Schwarz, Helmut (April 1994). "Experimental evidence for the gas phase existence of HSOH (hydrogen thioperoxide) and SOH2 (thiooxonium ylide)". Chemical Physics Letters. 221 (5–6): 359–362. Bibcode:1994CPL...221..359I. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(94)00293-2.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Winnewisser-2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page).