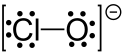
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hypochlorite
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Chlorate(I) | |
| Other names
Chloroxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.235.795 |
| 682 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3212 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Conjugate acid | Hypochlorous acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
In chemistry, hypochlorite, or chloroxide is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite (household bleach) and calcium hypochlorite (a component of bleaching powder, swimming pool "chlorine").[1] The Cl-O distance in ClO− is 1.69 Å.[2]
The name can also refer to esters of hypochlorous acid, namely organic compounds with a ClO– group covalently bound to the rest of the molecule. The principal example is tert-butyl hypochlorite, which is a useful chlorinating agent.[3]
Most hypochlorite salts are handled as aqueous solutions. Their primary applications are as bleaching, disinfection, and water treatment agents. They are also used in chemistry for chlorination and oxidation reactions.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Topić, Filip; Marrett, Joseph M.; Borchers, Tristan H.; Titi, Hatem M.; Barrett, Christopher J.; Friščić, Tomislav (2021). "After 200 Years: The Structure of Bleach and Characterization of Hypohalite Ions by Single-Crystal X-Ray Diffraction". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60 (46): 24400–24405. doi:10.1002/anie.202108843. PMID 34293249. S2CID 236199263.
- ^ Mintz, M. J.; C. Walling (1969). "t-Butyl hypochlorite". Organic Syntheses. 49: 9. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.049.0009.