| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazol-2-ylidene | |
| Other names
1,3-Dimesitylimidazol-2-ylidene, 1,3-bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-imidazolium, 1,3-bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.154.201 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24N2 | |
| Molar mass | 304.43 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 150 to 155 °C (302 to 311 °F; 423 to 428 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
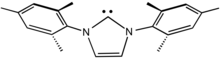
IMes is an abbreviation for an organic compound that is a common ligand in organometallic chemistry. It is an N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC). The compound, a white solid, is often not isolated but instead is generated upon attachment to the metal centre.[1]
First prepared by Arduengo,[2] the heterocycle is synthesized by condensation of 2,4,6-trimethylaniline and glyoxal to give the diimine. In the presence of acid, the resulting glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine) condenses with formaldehyde to give the dimesitylimidazolium cation. This cation is the conjugate acid of the NHC.[3][4]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Nolanwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Arduengo, Anthony J.; Dias, H. V. Rasika; Harlow, Richard L.; Kline, Michael (1992). "Electronic stabilization of nucleophilic carbenes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 114 (14): 5530–5534. doi:10.1021/ja00040a007.
- ^ Ison, Elon A.; Ison, Ana (2012). "Synthesis of Well-Defined Copper N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes and Their Use as Catalysts for a "Click Reaction": A Multistep Experiment That Emphasizes the Role of Catalysis in Green Chemistry". Journal of Chemical Education. 89 (12): 1575–1577. Bibcode:2012JChEd..89.1575I. doi:10.1021/ed300243s.
- ^ Chen, Junting; Ritter, Tobias (2019). "Late-Stage Deoxyfluorination of Phenols with PhenoFluorMix". Org. Synth. 96: 16. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.096.0016.