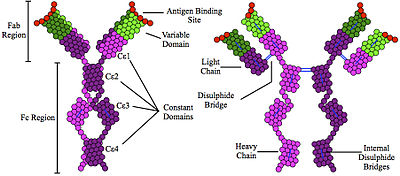


Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) "isotype") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε chain containing four Ig-like constant domains (Cε1–Cε4).[1] IgE is thought to be an important part of the immune response against infection by certain parasitic worms, including Schistosoma mansoni, Trichinella spiralis,[2][3] and Fasciola hepatica.[4] IgE is also utilized during immune defense against certain protozoan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum.[5] IgE may have evolved as a defense to protect against venoms.[6][7][8]
IgE also has an essential role in type I hypersensitivity,[9] which manifests in various allergic diseases, such as allergic asthma, most types of sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, food allergies, and specific types of chronic urticaria and atopic dermatitis. IgE also plays a pivotal role in responses to allergens, such as anaphylactic reactions to drugs, bee stings, and antigen preparations used in desensitization immunotherapy.
IgE is typically the least abundant isotype: blood serum IgE levels in a non-atopic individual are only 0.05% of the Ig concentration,[10] compared to 75% for the IgGs at 10 mg/ml. Despite this, it is capable of triggering anaphylaxis, one of the most rapid and severe immunological reactions.[11]
- ^ "Antibody structure". Archived from the original on September 6, 2008.
- ^ Erb KJ (May 2007). "Helminths, allergic disorders and IgE-mediated immune responses: where do we stand?". European Journal of Immunology. 37 (5): 1170–3. doi:10.1002/eji.200737314. PMID 17447233. S2CID 24519249.
- ^ Watanabe N, Bruschi F, Korenaga M (April 2005). "IgE: a question of protective immunity in Trichinella spiralis infection". Trends in Parasitology. 21 (4): 175–8. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2005.02.010. PMID 15780839.
- ^ Pfister K, Turner K, Currie A, Hall E, Jarrett EE (November 1983). "IgE production in rat fascioliasis". Parasite Immunology. 5 (6): 587–93. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00775.x. PMID 6657297. S2CID 1530964.
- ^ Duarte J, Deshpande P, Guiyedi V, Mécheri S, Fesel C, Cazenave PA, et al. (January 2007). "Total and functional parasite specific IgE responses in Plasmodium falciparum-infected patients exhibiting different clinical status". Malaria Journal. 6: 1. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-6-1. PMC 1781948. PMID 17204149.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Marichal T, Starkl P, Reber LL, Kalesnikoff J, Oettgen HC, Tsai M, et al. (November 2013). "A beneficial role for immunoglobulin E in host defense against honeybee venom". Immunity. 39 (5): 963–75. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.005. PMC 4164235. PMID 24210352.
- ^ Gould HJ, Sutton BJ, Beavil AJ, Beavil RL, McCloskey N, Coker HA, et al. (2003). "The biology of IGE and the basis of allergic disease". Annual Review of Immunology. 21: 579–628. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141103. PMID 12500981.
- ^ Winter WE, Hardt NS, Fuhrman S (September 2000). "Immunoglobulin E: importance in parasitic infections and hypersensitivity responses". Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. 124 (9): 1382–5. doi:10.5858/2000-124-1382-IE. PMID 10975945.
- ^ Reber, LL; Hernandez, JD; Galli, SJ (August 2017). "The pathophysiology of anaphylaxis". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 140 (2): 335–348. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.06.003. PMC 5657389. PMID 28780941.