| Intercalated disc | |
|---|---|
 Cardiac muscle, an intercalated disc can be seen joining cardiomyocytes in magnified section | |
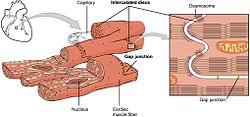 Intercalated discs, desmosomes and gap junctions in cardiac muscle fiber. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Cardiac muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | discus intercalaris, discus intercalatus |
| TH | H2.00.05.2.02006 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy | |
Intercalated discs or lines of Eberth are microscopic identifying features of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional syncytium. By contrast, skeletal muscle consists of multinucleated muscle fibers and exhibits no intercalated discs. Intercalated discs support synchronized contraction of cardiac tissue in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work like a pump.[1] They occur at the Z line of the sarcomere and can be visualized easily when observing a longitudinal section of the tissue.
- ^
 This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license. Betts, J Gordon; Desaix, Peter; Johnson, Eddie; Johnson, Jody E; Korol, Oksana; Kruse, Dean; Poe, Brandon; Wise, James; Womble, Mark D; Young, Kelly A (June 8, 2023). Anatomy & Physiology. Houston: OpenStax CNX. 10.7 Cardiac muscle tissue. ISBN 978-1-947172-04-3.
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license. Betts, J Gordon; Desaix, Peter; Johnson, Eddie; Johnson, Jody E; Korol, Oksana; Kruse, Dean; Poe, Brandon; Wise, James; Womble, Mark D; Young, Kelly A (June 8, 2023). Anatomy & Physiology. Houston: OpenStax CNX. 10.7 Cardiac muscle tissue. ISBN 978-1-947172-04-3.