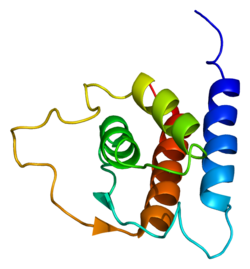
Interleukin 13 (IL-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL13 gene.[4][5][6] IL-13 was first cloned in 1993 and is located on chromosome 5q31.1 with a length of 1.4kb.[4] It has a mass of 13 kDa and folds into 4 alpha helical bundles.[7] The secondary structural features of IL-13 are similar to that of Interleukin 4 (IL-4); however it only has 25% sequence identity to IL-4 and is capable of IL-4 independent signaling.[7][4][8] IL-13 is a cytokine secreted by T helper type 2 (Th2) cells, CD4 cells, natural killer T cell, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils and nuocytes.[7] Interleukin-13 is a central regulator in IgE synthesis, goblet cell hyperplasia, mucus hypersecretion, airway hyperresponsiveness, fibrosis and chitinase up-regulation.[7] It is a mediator of allergic inflammation and different diseases including asthma,[7] and atopic dermatitis.[9]
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020383 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b c Minty A, Chalon P, Derocq JM, Dumont X, Guillemot JC, Kaghad M, et al. (March 1993). "Interleukin-13 is a new human lymphokine regulating inflammatory and immune responses". Nature. 362 (6417): 248–250. Bibcode:1993Natur.362..248M. doi:10.1038/362248a0. PMID 8096327. S2CID 4368915.
- ^ McKenzie AN, Culpepper JA, de Waal Malefyt R, Brière F, Punnonen J, Aversa G, et al. (April 1993). "Interleukin 13, a T-cell-derived cytokine that regulates human monocyte and B-cell function". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (8): 3735–3739. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.3735M. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.8.3735. PMC 46376. PMID 8097324.
- ^ Morgan JG, Dolganov GM, Robbins SE, Hinton LM, Lovett M (October 1992). "The selective isolation of novel cDNAs encoded by the regions surrounding the human interleukin 4 and 5 genes". Nucleic Acids Research. 20 (19): 5173–5179. doi:10.1093/nar/20.19.5173. PMC 334302. PMID 1408833.
- ^ a b c d e Rael EL, Lockey RF (March 2011). "Interleukin-13 signaling and its role in asthma". The World Allergy Organization Journal. 4 (3): 54–64. doi:10.1097/WOX.0b013e31821188e0. PMC 3651056. PMID 23283176.
- ^ Zurawski G, de Vries JE (January 1994). "Interleukin 13, an interleukin 4-like cytokine that acts on monocytes and B cells, but not on T cells". Immunology Today. 15 (1): 19–26. doi:10.1016/0167-5699(94)90021-3. PMID 7907877.
- ^ Dekkers C, de Bruin-Weller M (2024). "The pleiotropic role of IL-13 in AD pathogenesis". The British Journal of Dermatology. 15 (1): 19–26. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljae174. PMID 38659397.