| Internal anal sphincter | |
|---|---|
 Coronal section through the anal canal. B. Cavity of urinary bladder V.D. Vas deferens. S.V. Seminal vesicle. R. Second part of rectum. A.C. Anal canal. L.A. Levator ani. I.S. Internal anal sphincter. E.S. External anal sphincter. | |
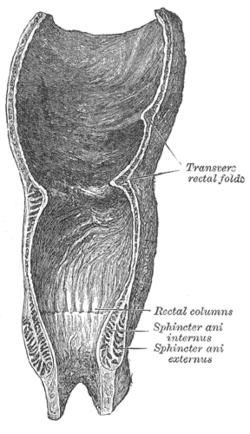 Coronal section of rectum and anal canal | |
| Details | |
| Nerve | Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S4), thoracicolumbar outflow of the spinal cord |
| Actions | Keeps the anal canal and orifice closed, aids in the expulsion of the feces |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus sphincter ani internus |
| TA98 | A05.7.05.011 |
| TA2 | 3018 |
| FMA | 15710 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The internal anal sphincter, IAS, or sphincter ani internus is a ring of smooth muscle that surrounds about 2.5–4.0 cm of the anal canal. It is about 5 mm thick, and is formed by an aggregation of the smooth (involuntary) circular muscle fibers of the rectum. It terminates distally about 6 mm from the anal orifice.[citation needed]
The internal anal sphincter aids the sphincter ani externus to occlude the anal aperture and aids in the expulsion of the feces. Its action is entirely involuntary. It is normally in a state of continuous maximal contraction to prevent leakage of faeces or gases. Sympathetic stimulation stimulates and maintains the sphincter's contraction, and parasympathetic stimulation inhibits it. It becomes relaxed in response to distention of the rectal ampulla, requiring voluntary contraction of the puborectalis and external anal sphincter to maintain continence,[1] and also contracts during the bulbospongiosus reflex.[2][3][4][5]
- ^ Moore, K., Dalley, A., Agur, A. "Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 6th Edition.
- ^ Vodušek DB, Deletis V (2002). "Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring of the Sacral Nervous System". Neurophysiology in Neurosurgery, A Modern Intraoperative Approach: 153–165. doi:10.1016/B978-012209036-3/50011-1. ISBN 9780122090363. S2CID 78605592.
- ^ Sarica Y, Karacan I (July 1987). "Bulbocavernosus reflex to somatic and visceral nerve stimulation in normal subjects and in diabetics with erectile impotence". The Journal of Urology. 138 (1): 55–58. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(17)42987-9. PMID 3599220.
- ^ Jiang XZ, Zhou CK, Guo LH, Chen J, Wang HQ, Zhang DQ, et al. (December 2009). "[Role of bulbocavernosus reflex to stimulation of prostatic urethra in pathologic mechanism of primary premature ejaculation]". Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (in Chinese). 89 (46): 3249–3252. PMID 20193361.
- ^ Podnar S (February 2012). "Clinical elicitation of the penilo-cavernosus reflex in circumcised men". BJU International. 109 (4): 582–585. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10364.x. PMID 21883821. S2CID 27143105.