| Internal urethral sphincter | |
|---|---|
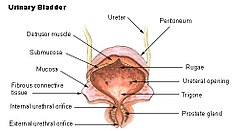 The urinary bladder, with the position of the internal urethral sphincter shown as the internal urethral orifice. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | The inferior ramus of the pubic bone |
| Insertion | Perineal raphe |
| Nerve | Sympathetic fibers from T10-L2 through the inferior hypogastric plexus then vesical nervous plexus |
| Actions | Constricts proximal urethra, maintains urinary continence |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus sphincter urethrae internus |
| TA98 | A09.2.03.009 A09.4.02.013 |
| TA2 | 3444, 3428 |
| FMA | 45769 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The internal urethral sphincter is a urethral sphincter muscle which constricts the internal urethral orifice. It is located at the junction of the urethra with the urinary bladder and is continuous with the detrusor muscle,[1][2] but anatomically and functionally fully independent from it.[3] It is composed of smooth muscle, so it is under the control of the autonomic nervous system, specifically the sympathetic nervous system.
- ^ Jung J, Ahn HK, and Huh Y (September 2012). "Clinical and Functional Anatomy of the Urethral Sphincter". International Neurourology Journal. 16 (3): 102–106. doi:10.5213/inj.2012.16.3.102. PMC 3469827. PMID 23094214.
- ^ Sam P, LaGrange CA (February 2019). "Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Sphincter Urethrae". StatPearls [Internet]. PMID 29494045.
- ^ Dorschner W, Stolzenburg JU, Neuhaus J (2001). "Structure and function of the bladder neck". Advances in Anatomy, Embryology, and Cell Biology. 159: III–XII, 1–109. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-56879-4. ISBN 978-3-540-67998-1. PMID 11417142. S2CID 36907268., page 29, Preview Amazon.