| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
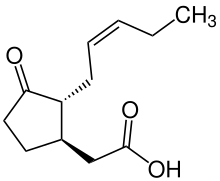
| Preferred IUPAC name
{(1R,2R)-3-Oxo-2-[(2Z)-pent-2-en-1-yl]cyclopentyl}acetic acid | |
| Other names
Jasmonic acid
(−)-Jasmonic acid JA (1R,2R)-3-Oxo-2-(2Z)-2-pentenylcyclopentylethanoic acid {(1R,2R)-3-Oxo-2-[(2Z)-2-penten-1-yl]cyclopentyl}acetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H18O3 | |
| Molar mass | 210.27 g/mol |
| Density | 1.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) at 0.7 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Jasmonic acid (JA) is an organic compound found in several plants including jasmine. The molecule is a member of the jasmonate class of plant hormones. It is biosynthesized from linolenic acid by the octadecanoid pathway. It was first isolated in 1957 as the methyl ester of jasmonic acid by the Swiss chemist Édouard Demole and his colleagues.[1]
- ^ Demole, E.; Lederer, E.; Mercier, D. (1962). "Isolement et determination de la structure du jasmonate de methyle, constituent odorant characteristique de l'essence de jasmin" [Isolation and determination of the structure of methyl jasmonate, the aromatic constituent characteristic of jasmine essential oil]. Helvetica Chimica Acta (in French). 45 (2): 675–685. doi:10.1002/hlca.19620450233.
- Chapuis, Christian (December 2011). "The chemistry and creative legacy of methyl jasmonate and hedione". Perfumer & Flavorist. 36: 36–48.