| Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Long QT interval-deafness syndrome[1] |
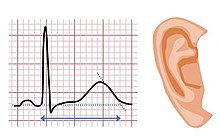 | |
| The features of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome include a prolonged QT interval and sensorineural deafness | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Blackouts, seizures, sensorineural deafness |
| Complications | Sudden death |
| Usual onset | Congenital |
| Causes | Genetic |
| Differential diagnosis | Other forms of Long QT syndrome |
| Treatment | Beta blockers, implantable cardioverter defibrillator |
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is a rare type of long QT syndrome associated with severe, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss.[2] Those with JLNS are at risk of abnormal heart rhythms called arrhythmias, which can lead to fainting, seizures, or sudden death. JLNS, like other forms of long QT syndrome, causes the cardiac muscle to take longer than usual to recharge between beats. It is caused by genetic variants responsible for producing ion channels that carry transport potassium out of cells. The condition is usually diagnosed using an electrocardiogram, but genetic testing can also be used. Treatment includes lifestyle measures, beta blockers, and implantation of a defibrillator in some cases. It was first described by Anton Jervell and Fred Lange-Nielsen in 1957.[3]
- ^ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Jervell and Lange Nielsen syndrome". www.orpha.net. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Tester in EDHwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Jervell, A.; Lange-Nielsen, F. (1957). "Congenital deaf-mutism, functional heart disease with prolongation of the Q-T interval, and sudden death". American Heart Journal. 54 (1): 59–68. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(57)90079-0. PMID 13435203.