| Ji–Lu Mandarin | |
|---|---|
| Beifang Mandarin | |
| Region | Hebei, Shandong |
Native speakers | (84 million cited 1982)[1] 12.6% of all Mandarin |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| ISO 639-6 | jlua |
cmn-jil | |
| Glottolog | jilu1239 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-be |
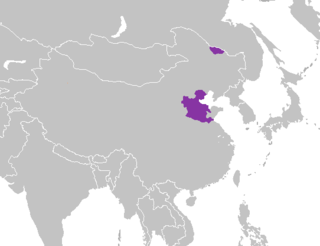 | |
Jilu or Ji–Lu Mandarin, formerly known as Beifang Mandarin "Northern Mandarin", is a dialect of Mandarin Chinese spoken in the Chinese provinces of Hebei (冀, Jì) and the western part of Shandong (魯, Lǔ) and Xunke, Tangwang & Jiayin counties of Heilongjiang. Its name is a combination of the abbreviated names of the two provinces, which derive from ancient local provinces.[2] The names are combined as Ji–Lu Mandarin.
Although these areas are near Beijing, Ji–Lu has a different accent and many lexical differences from the Beijing dialect, which is the basis for Standard Chinese, the official national language. There are three dialect groups: Bao–Tang, Shi–Ji, and Cang–Hui.[3][4]
People from the eastern part of Shandong, or the Jiaodong Peninsula, speak Jiaoliao Mandarin.
- ^ Keith Brown Encyclopedia of Language & Linguistics 2007 Elsevier ISBN 0-08-044299-4 Gu Y 2 page 344
- ^ 现代汉语方言大词典 (The Great Dictionary of Modern Chinese Dialects) 2002 Jiangsu Educational Publishers (2002 12 1 ) ISBN 7534350808
- ^ Maria Kurpaska Chinese Language(s): A Look through the Prism of The Great Dictionary of Modern Chinese Dialects 2010 Page 79 "5.1.3. Ji–Lu Mandarin group (冀鲁官话区 Jìlǔ Guānhuàqū) (cf. Atlas: Bl, B2, B3, B7; You Rujie 2004: 7)54 The A and B features of the Beijing Mandarin group are also true for the Ji–Lu Mandarin group. The main differences between the Beijing ..."
- ^ Cahiers de linguistique: Asie orientale - Volume 37, Issues 1-2 2008 -- Page 32 "Therefore, given that the uses of gei as a direct object marker or an agent marker do not appear to be typical for other dialects of the Greater Beijing Mandarin and Jì-Lǔ Mandarin area, and that it is attested at best sporadically in earlier ..."